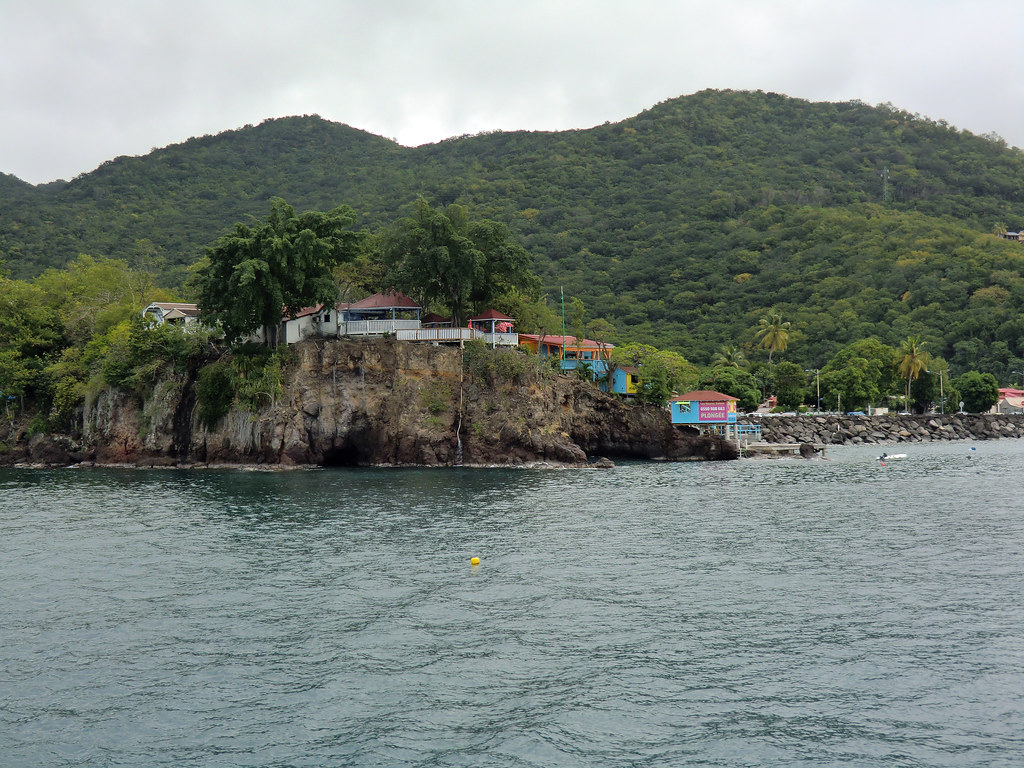Post by Dominicanese on Jan 3, 2018 15:13:14 GMT
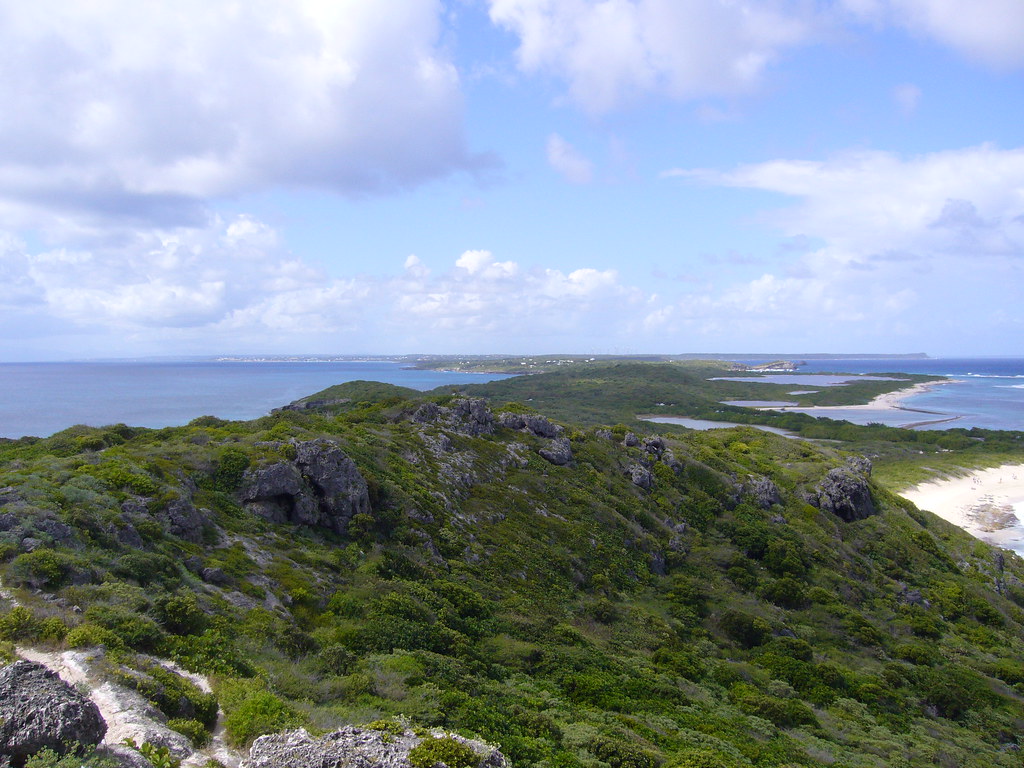
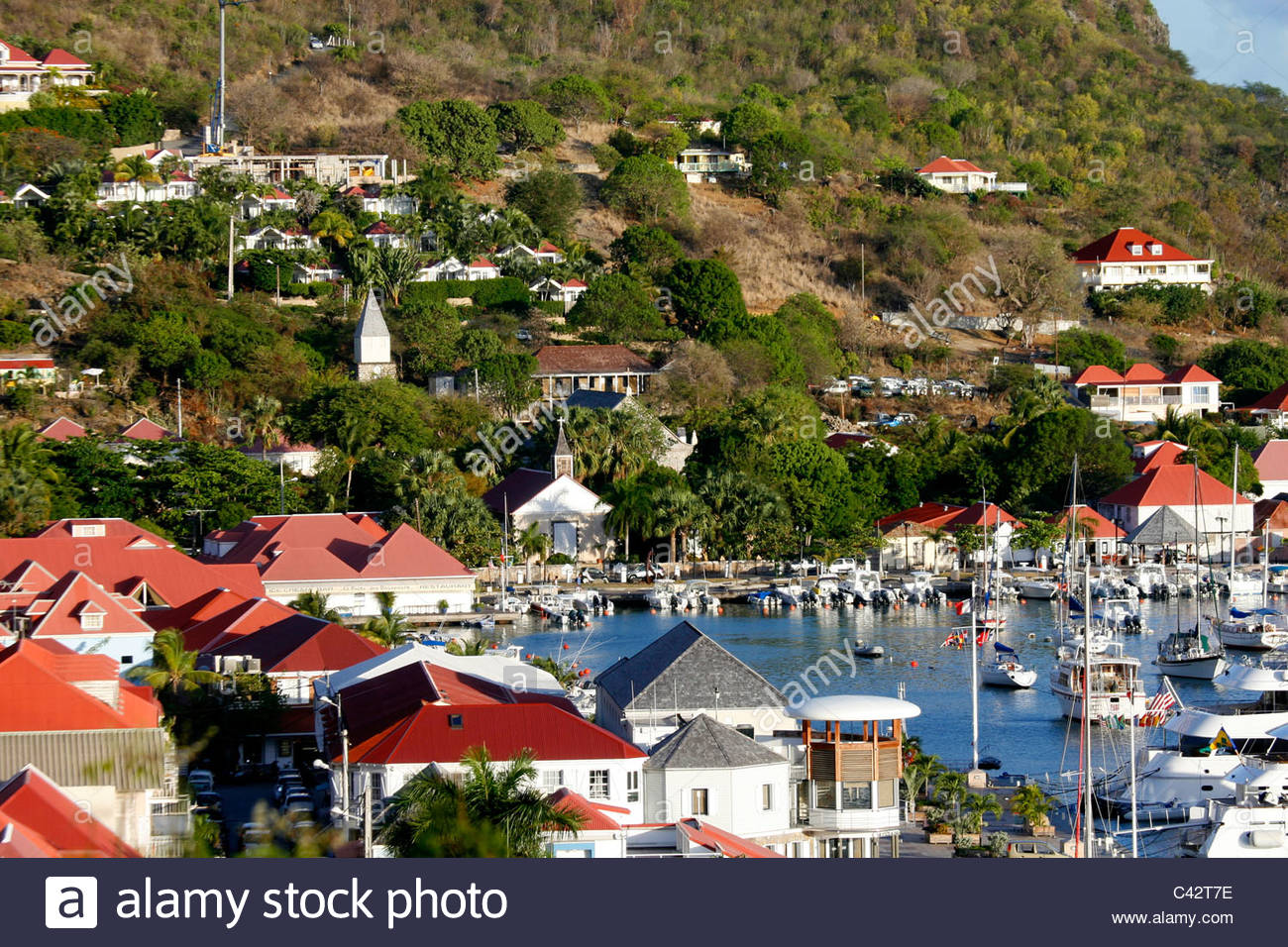
Guadeloupe.








/IMG_0396-5894d5ee5f9b5874ee1dffc6.JPG)


Culture:
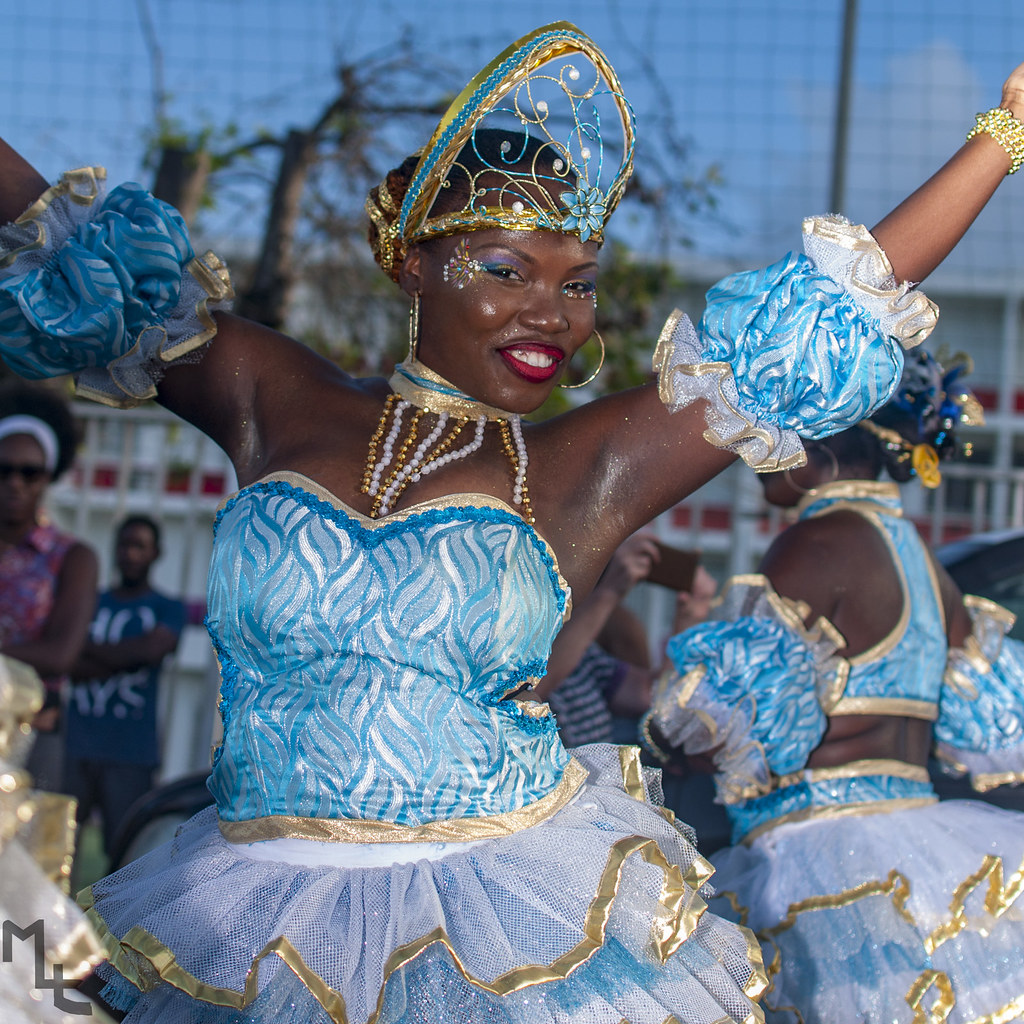
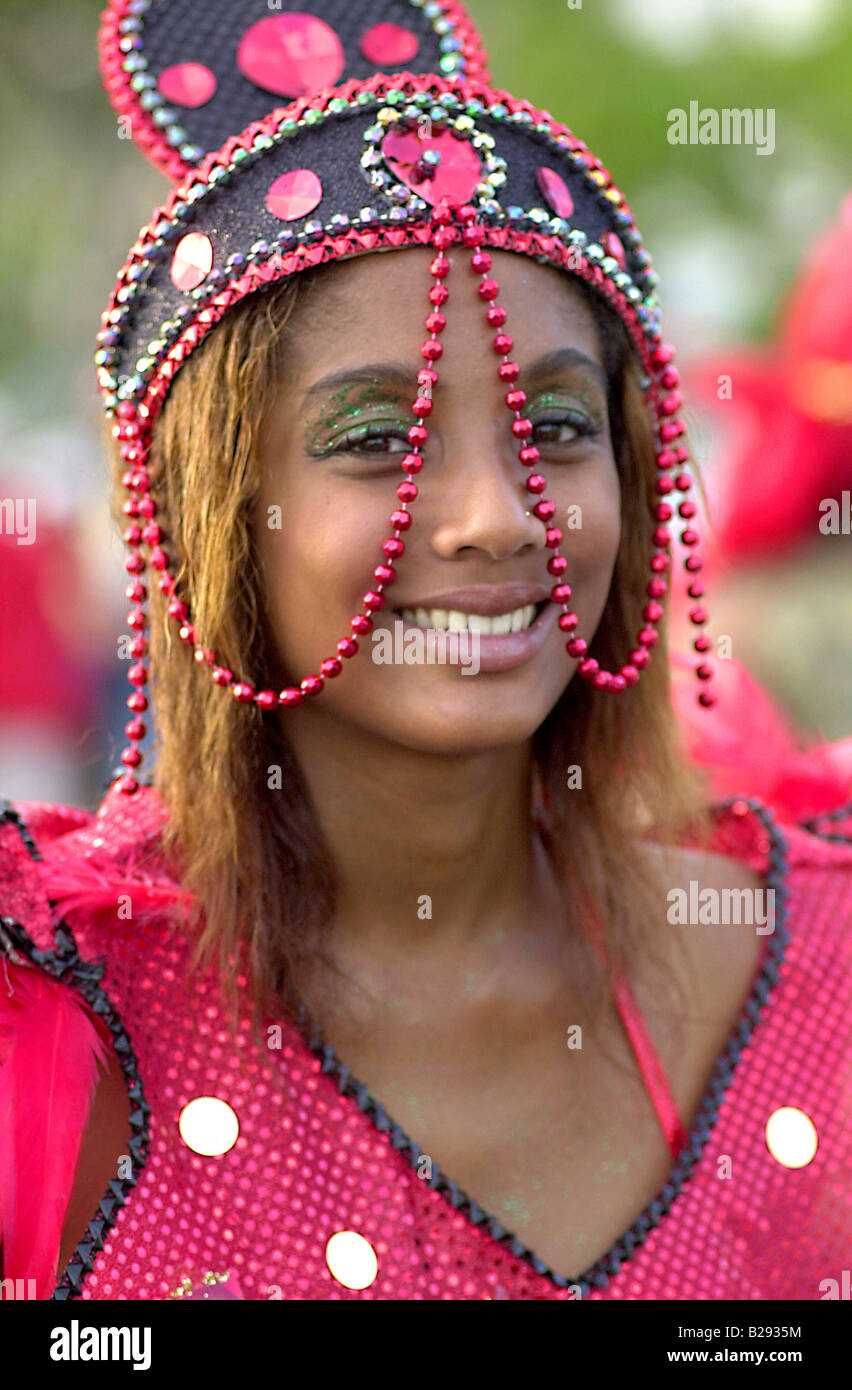
Guadeloupe is a melting pot of cultures. Its art, music, dance, and culinary traditions have been influenced by France, Africa, India, and its neighbors in the Caribbean. The majority of the locals are Roman Catholic, with a predominantly Evangelical Protestant minority.
Cuisine:
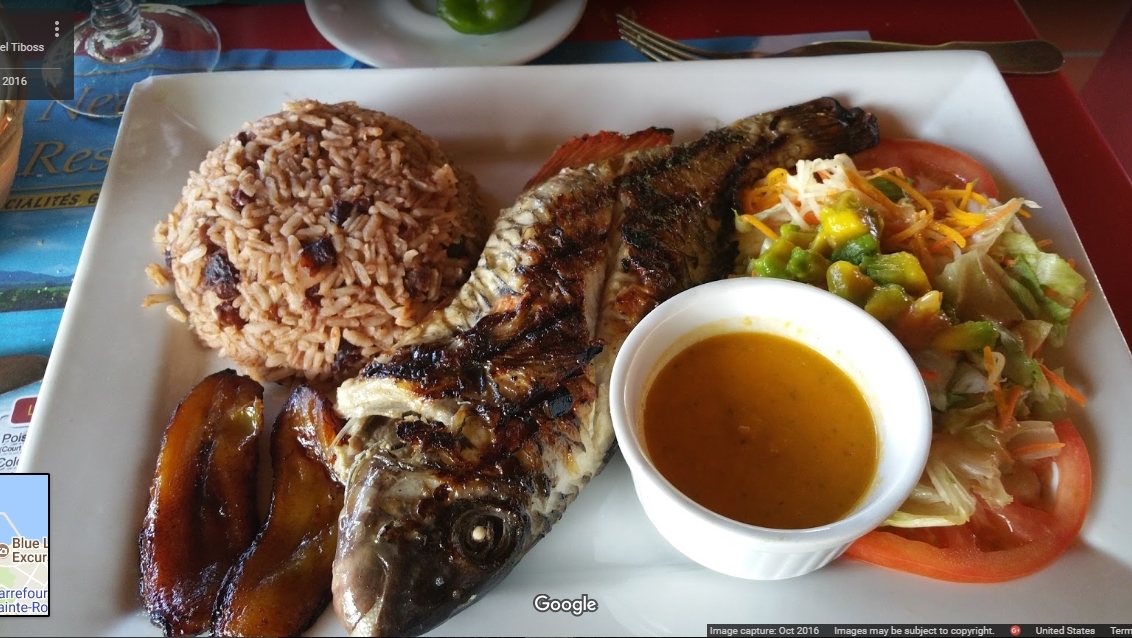
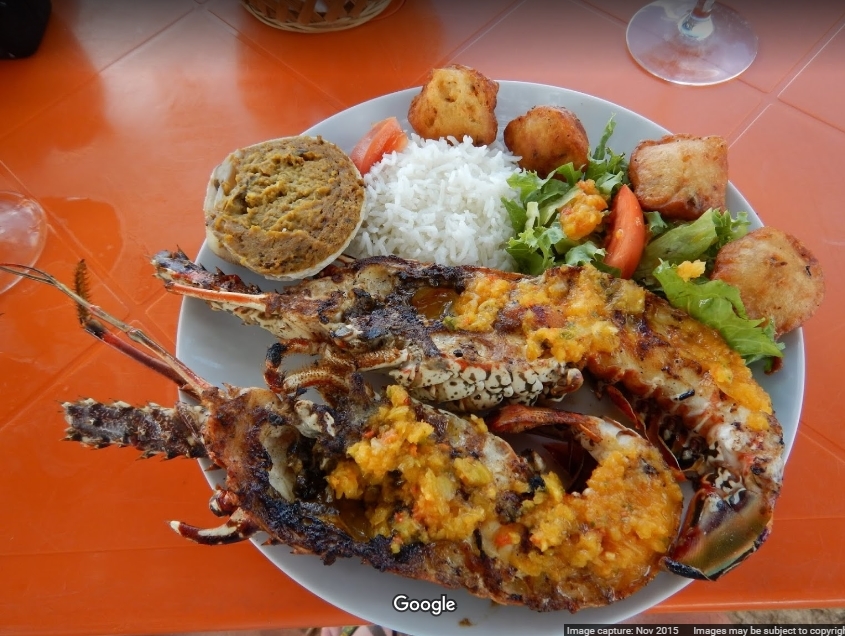
Guadeloupe is an Island governed by the French, but despite this its cuisine represents a unique mix with European, East Indian and African influences. Many people came in this country and brought all kind of ingredients and special methods of cooking and preparing the dishes. In 1635 the French took possession over this beautiful country and introduced to the natives the costume of growing cattle. Over the next centuries due to the prosperity of the Island, the British people tried to conquer it several times and steal it from the French. They failed to accomplish that. Beside the French and British influences Guadeloupe cuisine adopted many dishes and ingredients from the Indian people and the Arabs. Varied types of peppers and other spices typically Indian are being used nowadays in the Guadeloupe cuisine. A distinctive part of this country cuisine is represented by the Creole cuisine.

Creole cuisine can be served anyplace any anytime in Guadeloupe. This special part of the traditional Guadelupe cuisine represents a delicious and spectacular mix of African, Arabic, French and Indian influences. Special recipes that have been passed from generation to generation are made with fresh seafood and poultry and can be sometimes so hot and spicy that hardly can one handle them. Local Guadeloupe cuisine is also famous for the great usage of fresh fruits and seafood. Using these healthy and natural ingredients great and tasteful salads, appetizers and dessert are made. Other specialties made with seafood and served in this country include smoked fish, shellfish, stuffed land crabs. All these dishes are seasoned with chilli sauces or curry dishes. In the Caribbean, Guadelupe cuisine is recognized as being one of the most spectacular due to the great number of recipes and dishes existing here but mostly due to the exquisite taste and flavors that of the food.
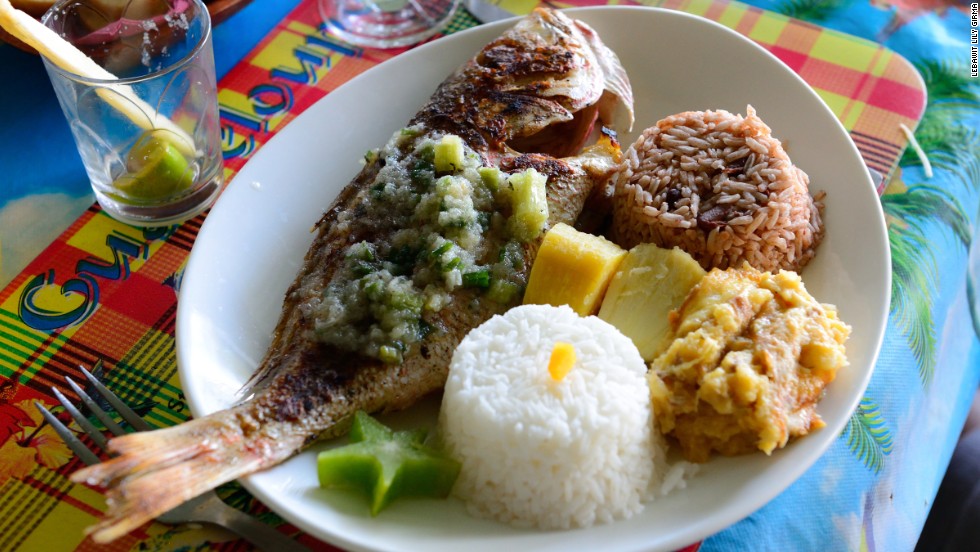

Most of the preparation methods existing in the Guadeloupe cuisine are being borrowed from their neighbors and adjusted to this country own traditional dishes. While there are no specific or unique preparation methods for Guadelupe cooking, we should point out that attention to detail is important in the Guadelupe cuisine. Using the right amount of spices for example is essential – either for spicing up the taste or for coloring the dish. The diversity of vegetables and cereals found in Guadelupe is also noticed in the delicious dishes belonging to their cuisine. The visual attractiveness of the dish is also important, and a balance between colors and proportion differentiates. Each traditional dish has a special cooking method, which is more or less general in all of Guadelupe’s regions. Meat is one of the main elements of most Guadelupe dishes and cured and smoked hams are often parts of delicious dishes.
/GettyImages-86499489-58adc11a3df78c345bdac6fc.jpg)
In order to produce the best and most sophisticated dishes Guadeloupe cuisine is using all kind of cooking tools ranging from cake pans, can openers, colanders, egg rings, poachers and holders, food dishers & portioners, food pans & food containers. Besides all this special equipment a true Guadeloupe chef might need other kitchen utensils, such as food scales, food scoops and fryer baskets & accessories. You should consider insulated food carriers if you are transporting the food and a full set of kitchen linens and uniforms if you wish to look like a pro. Here are a few other items that will come handy while cooking Guadelupe food: juicers, kitchen knives, kitchen slicers, kitchen thermometers, measuring cups & measuring spoons, miscellaneous utensils, mixing bowls and skimmers & strainers. Essential utensils like serving spoons, spatulas, forks, turners, scrapers and tongs should also be part of your cooking "arsenal".

Every festival and holiday held in Guadeloupe perfectly combine the exquisite tastes of homemade local food with the excitement of the celebration. Some of the most famous public holidays in Guadeloupe are New Year's Day, Good Friday, Ash Wednesday, Schoelcher Day, Ascension Day (May 12), All Souls' Day, Armistice Day (Nov 11) and Christmas. Every festival in this country range in length from at least two days to two weeks. Special traditional dishes are being cooked and served accompanied most of the time by the finest French wines. During any celebration the dish called Jambalaya can be easily found in any home, restaurant or household due to the fact that is very famous and incredible tasteful. It can be made with Chicken, Ham, Sausage, shrimp, fresh Pork, and oysters. To increase the flavor of the dish ingredients like rice, onions, pepper, tomatoes are often added.
Music:
The music of Guadeloupe encompasses a large popular music industry, which gained in international renown after the success of zouk music in the later 20th century. Zouk's popularity was particularly intense in France, where the genre became an important symbol of identity for Guadeloupe and Martinique. Zouk's origins are in the folk music of Guadeloupe and Martinique, especially Guadeloupan gwo ka and Martinican chouval bwa, and the pan-Caribbean calypso tradition.
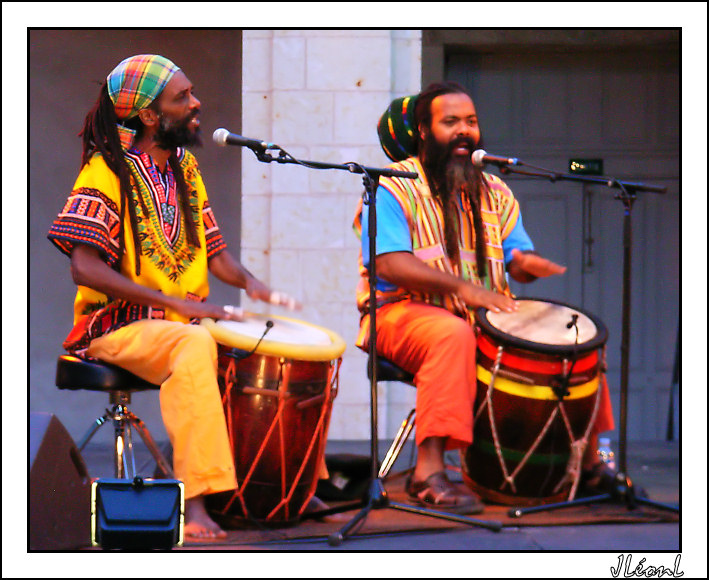

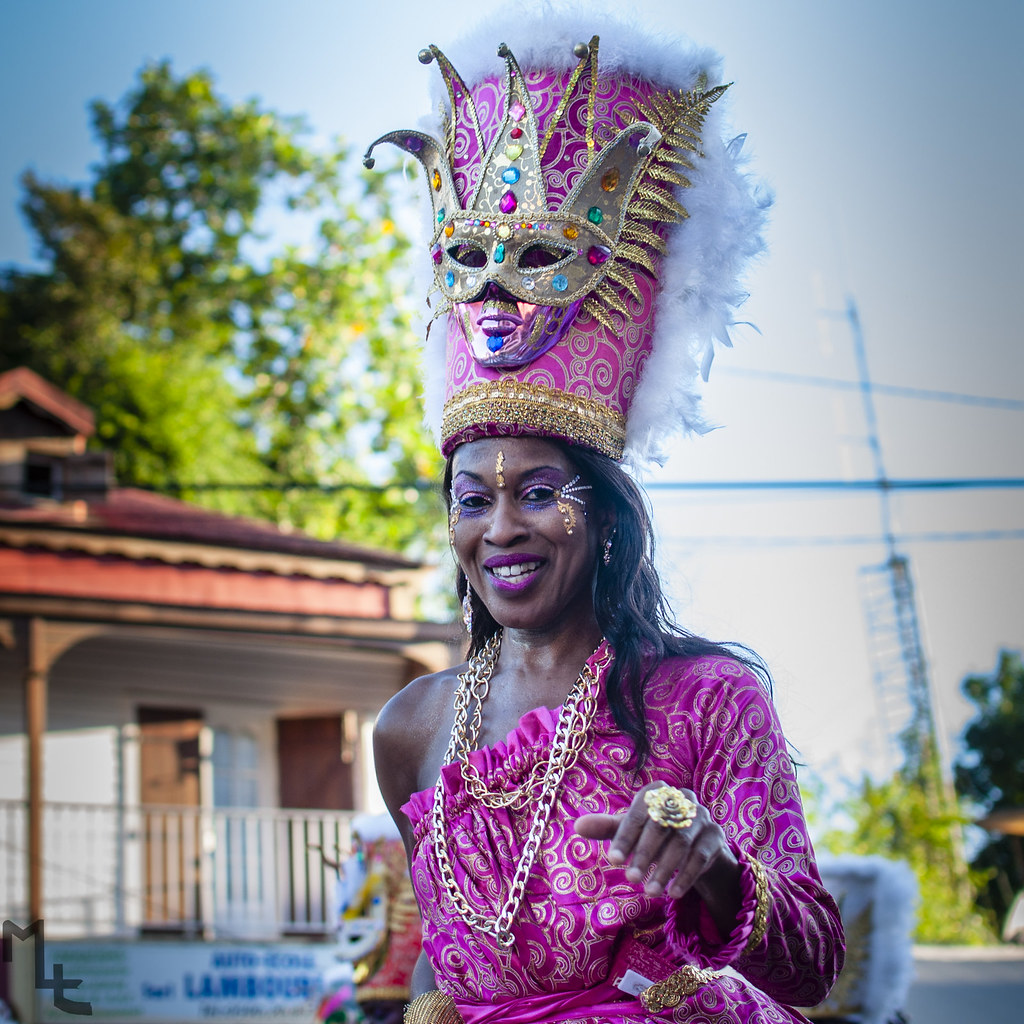
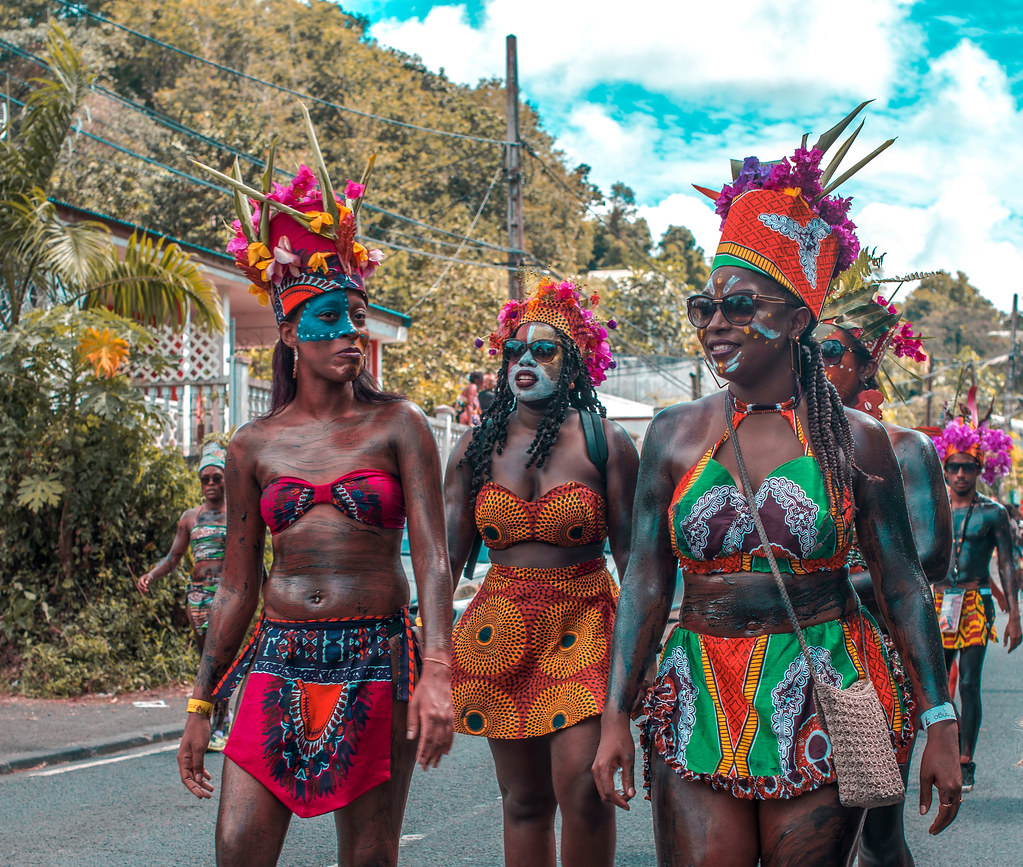
Carnival is a very important festival in Guadeloupe and Martinique. Music plays a vital role, with Guadeloupean gwo ka ensembles, zouk music and guadeloupean big bands marching across the island, and travelling and performing music known as C (or just videé) in a manner akin to Brazilian samba schools. Carnival in both islands declined following World War II, bouncing back with new band formats and new traditions only in the 1980s. Both islands feature participatory, call-and-response style songs during their Carnival celebrations.
Ethnic Racial Composition:
* 77% Mulatto
* 10% Black
* 10% White
* 2% Indian
* 1% Others
People:
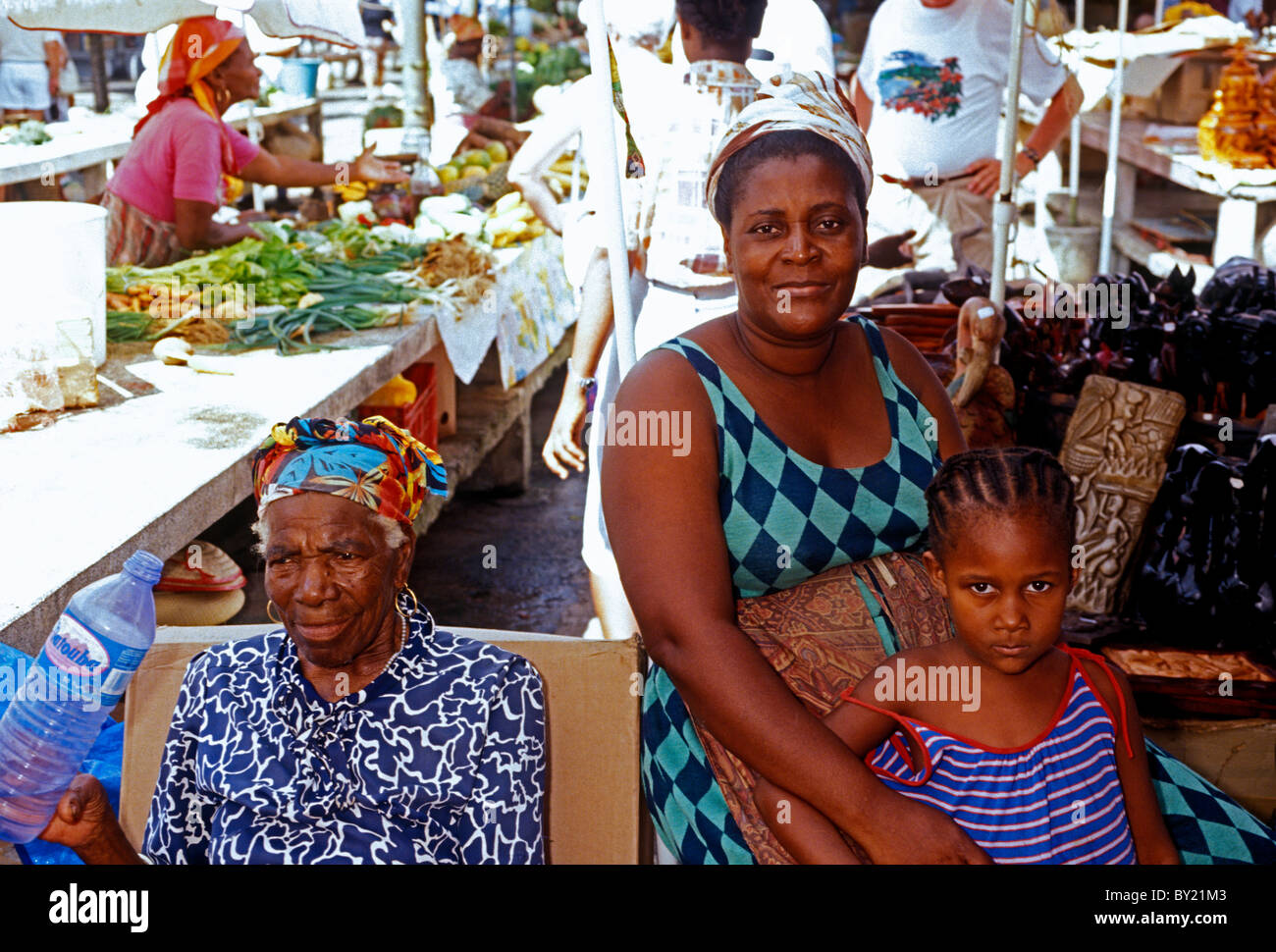
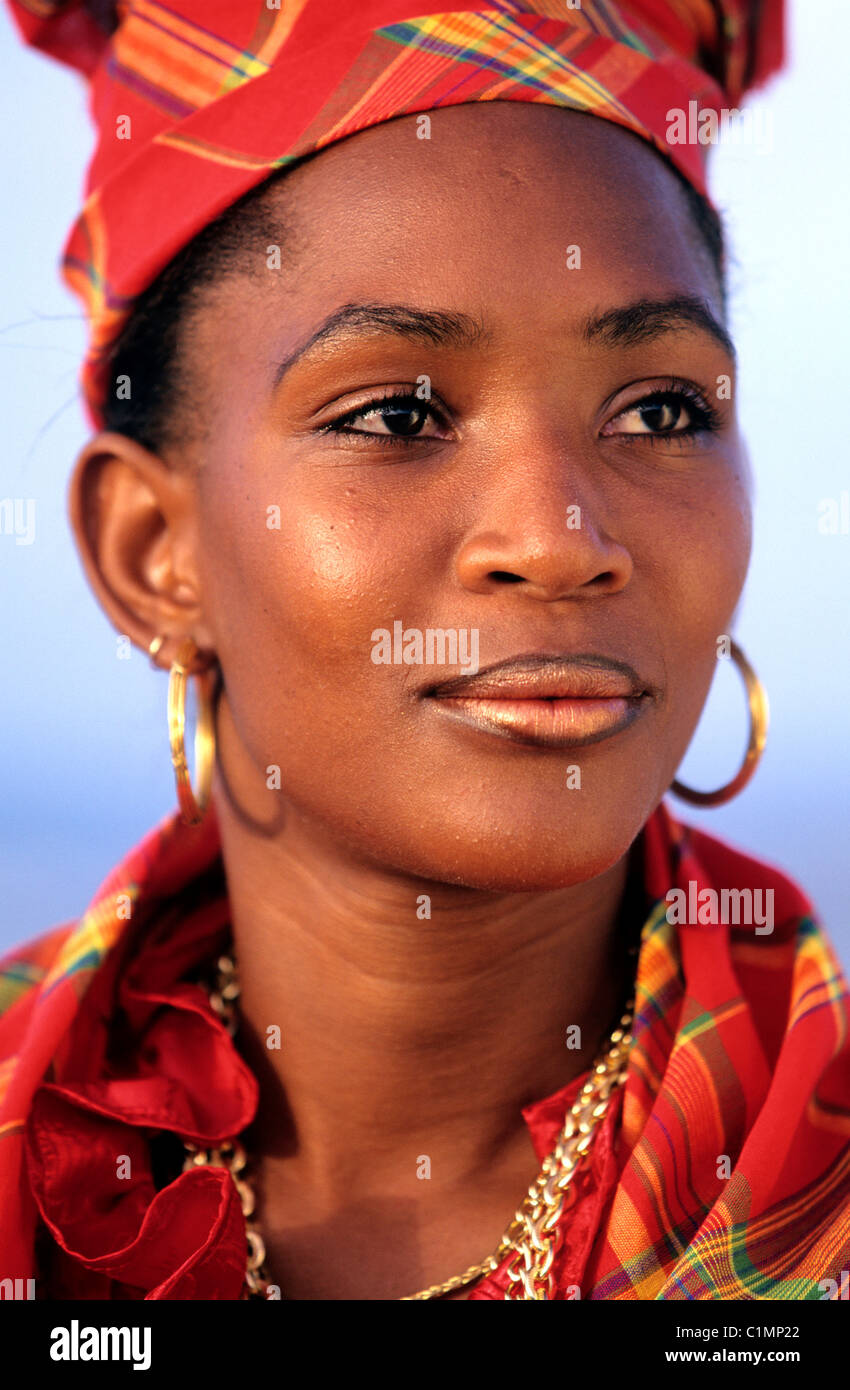
The population of Guadeloupe is mainly of African or mixed descent of Europeans, Indians (Tamil, Telugu, and other South Indians), Lebanese, Syrians, Chinese, and Carib Amerindians (remnants of the original pre-European population). The archipelago of Îles des Saintes is mostly populated by the descendants of colonists from Brittany and Normandy. It is largely Roman Catholic, speaking French and their dialect (Antillean French).

In 2012 the average population density in Guadeloupe was 247.7 inhabitants for every square kilometre, which is very high in comparison to the whole France's 116.5 inhabitants for every square kilometre. One third of the land is devoted to agriculture and all mountains are uninhabitable. This lack of space and shelter makes the population density even higher.
Languages:
French is the official language of Guadeloupe. They also speak a local dialect of French in informal situations and it is simply referred to as Guadeloupean French or Patois. Guadeloupean French stems mostly from Normandi French spoken in Northern France, with some influences from West African languages. There is also many words of Carib origin.
Religion:
The majority are Roman Catholic, with a minority of predominantly Evangelical Protestant groups.
Economy:
The economy of Guadeloupe depends on agriculture, tourism, light industry, and services. It also depends on mainland France for large subsidies and imports.
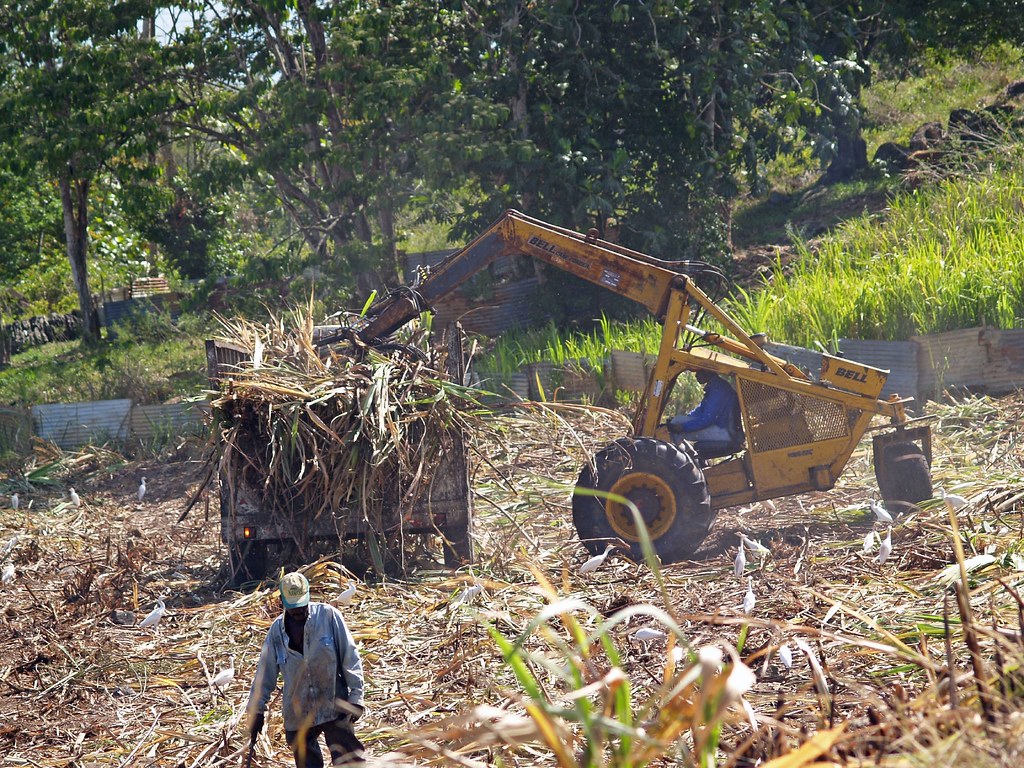
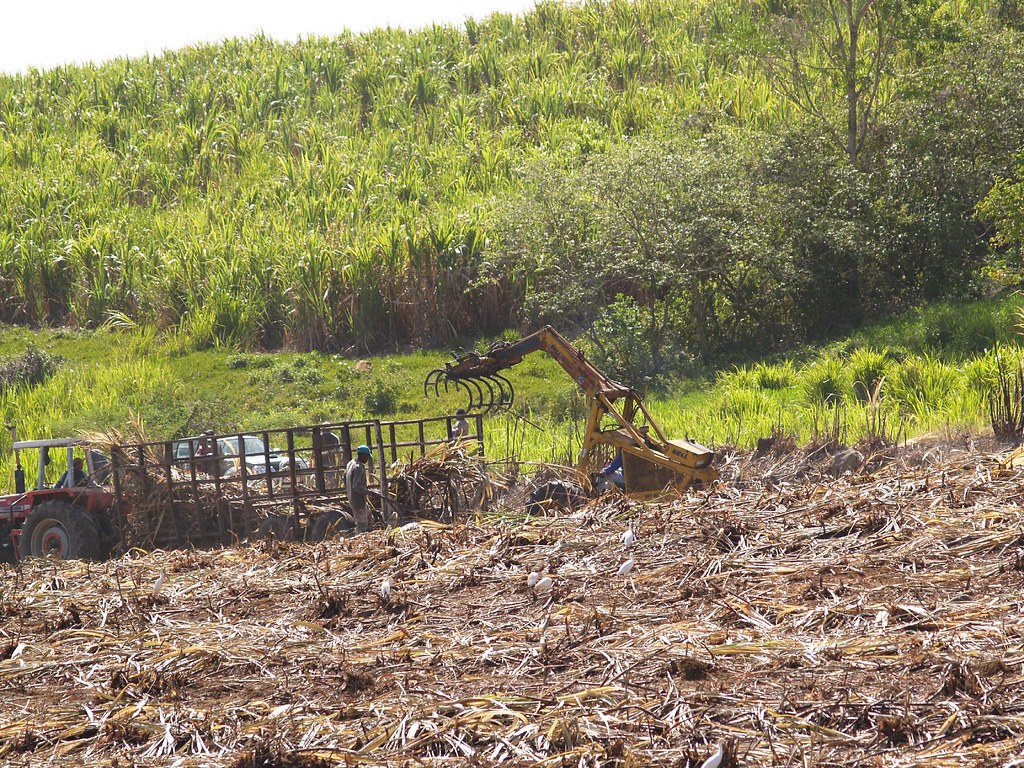
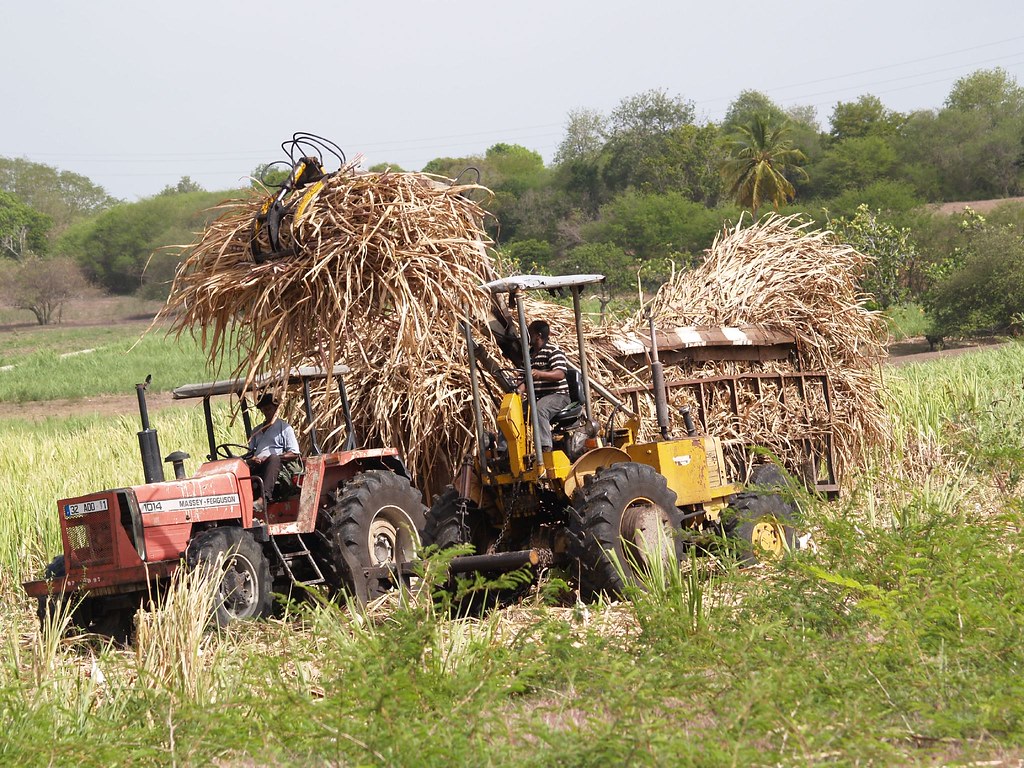
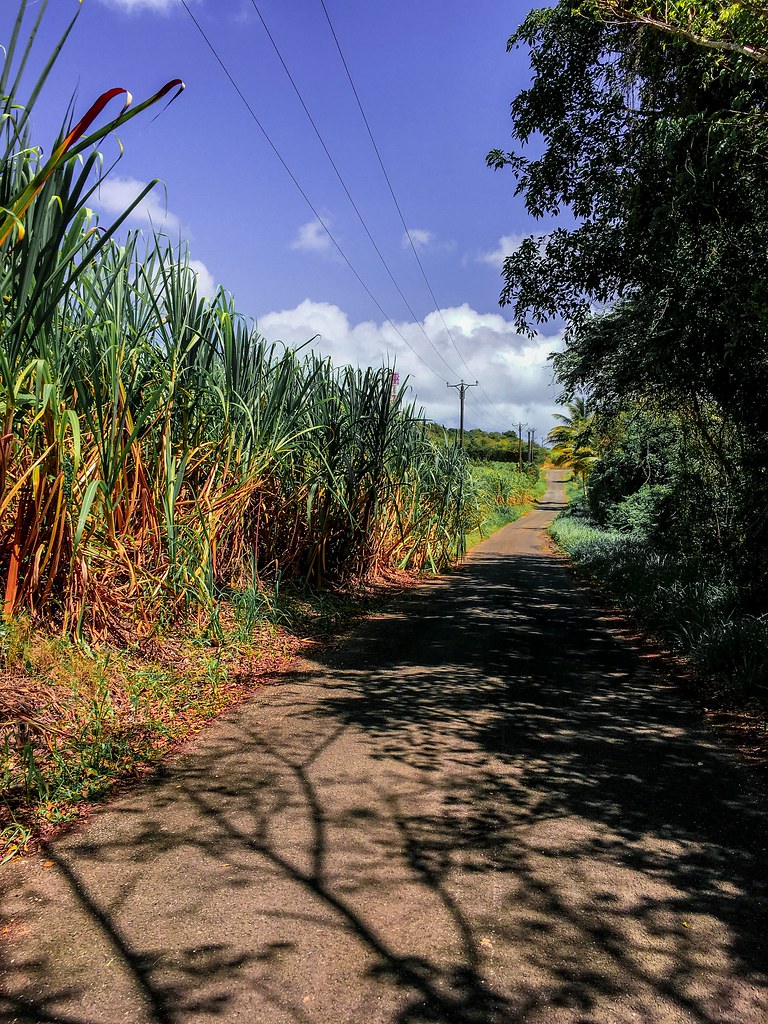
Tourism is a key industry; an increasingly large number of cruise ships visit the islands. The traditional sugarcane crop is slowly being replaced by other crops, such as bananas (which now supply about 50% of export earnings), eggplant, and flowers. Other vegetables and root crops are cultivated for local consumption, although Guadeloupe is still dependent on imported food, mainly from France. Light industry features sugar and rum production. Most manufactured goods and fuel are imported. Unemployment is especially high among the young. Hurricanes periodically devastate the economy.
Sports:
Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe.
Videos:










Culture:
Guadeloupe is a melting pot of cultures. Its art, music, dance, and culinary traditions have been influenced by France, Africa, India, and its neighbors in the Caribbean. The majority of the locals are Roman Catholic, with a predominantly Evangelical Protestant minority.
Cuisine:
Guadeloupe is an Island governed by the French, but despite this its cuisine represents a unique mix with European, East Indian and African influences. Many people came in this country and brought all kind of ingredients and special methods of cooking and preparing the dishes. In 1635 the French took possession over this beautiful country and introduced to the natives the costume of growing cattle. Over the next centuries due to the prosperity of the Island, the British people tried to conquer it several times and steal it from the French. They failed to accomplish that. Beside the French and British influences Guadeloupe cuisine adopted many dishes and ingredients from the Indian people and the Arabs. Varied types of peppers and other spices typically Indian are being used nowadays in the Guadeloupe cuisine. A distinctive part of this country cuisine is represented by the Creole cuisine.

Creole cuisine can be served anyplace any anytime in Guadeloupe. This special part of the traditional Guadelupe cuisine represents a delicious and spectacular mix of African, Arabic, French and Indian influences. Special recipes that have been passed from generation to generation are made with fresh seafood and poultry and can be sometimes so hot and spicy that hardly can one handle them. Local Guadeloupe cuisine is also famous for the great usage of fresh fruits and seafood. Using these healthy and natural ingredients great and tasteful salads, appetizers and dessert are made. Other specialties made with seafood and served in this country include smoked fish, shellfish, stuffed land crabs. All these dishes are seasoned with chilli sauces or curry dishes. In the Caribbean, Guadelupe cuisine is recognized as being one of the most spectacular due to the great number of recipes and dishes existing here but mostly due to the exquisite taste and flavors that of the food.

Most of the preparation methods existing in the Guadeloupe cuisine are being borrowed from their neighbors and adjusted to this country own traditional dishes. While there are no specific or unique preparation methods for Guadelupe cooking, we should point out that attention to detail is important in the Guadelupe cuisine. Using the right amount of spices for example is essential – either for spicing up the taste or for coloring the dish. The diversity of vegetables and cereals found in Guadelupe is also noticed in the delicious dishes belonging to their cuisine. The visual attractiveness of the dish is also important, and a balance between colors and proportion differentiates. Each traditional dish has a special cooking method, which is more or less general in all of Guadelupe’s regions. Meat is one of the main elements of most Guadelupe dishes and cured and smoked hams are often parts of delicious dishes.
/GettyImages-86499489-58adc11a3df78c345bdac6fc.jpg)
In order to produce the best and most sophisticated dishes Guadeloupe cuisine is using all kind of cooking tools ranging from cake pans, can openers, colanders, egg rings, poachers and holders, food dishers & portioners, food pans & food containers. Besides all this special equipment a true Guadeloupe chef might need other kitchen utensils, such as food scales, food scoops and fryer baskets & accessories. You should consider insulated food carriers if you are transporting the food and a full set of kitchen linens and uniforms if you wish to look like a pro. Here are a few other items that will come handy while cooking Guadelupe food: juicers, kitchen knives, kitchen slicers, kitchen thermometers, measuring cups & measuring spoons, miscellaneous utensils, mixing bowls and skimmers & strainers. Essential utensils like serving spoons, spatulas, forks, turners, scrapers and tongs should also be part of your cooking "arsenal".

Every festival and holiday held in Guadeloupe perfectly combine the exquisite tastes of homemade local food with the excitement of the celebration. Some of the most famous public holidays in Guadeloupe are New Year's Day, Good Friday, Ash Wednesday, Schoelcher Day, Ascension Day (May 12), All Souls' Day, Armistice Day (Nov 11) and Christmas. Every festival in this country range in length from at least two days to two weeks. Special traditional dishes are being cooked and served accompanied most of the time by the finest French wines. During any celebration the dish called Jambalaya can be easily found in any home, restaurant or household due to the fact that is very famous and incredible tasteful. It can be made with Chicken, Ham, Sausage, shrimp, fresh Pork, and oysters. To increase the flavor of the dish ingredients like rice, onions, pepper, tomatoes are often added.
Music:
The music of Guadeloupe encompasses a large popular music industry, which gained in international renown after the success of zouk music in the later 20th century. Zouk's popularity was particularly intense in France, where the genre became an important symbol of identity for Guadeloupe and Martinique. Zouk's origins are in the folk music of Guadeloupe and Martinique, especially Guadeloupan gwo ka and Martinican chouval bwa, and the pan-Caribbean calypso tradition.

Carnival is a very important festival in Guadeloupe and Martinique. Music plays a vital role, with Guadeloupean gwo ka ensembles, zouk music and guadeloupean big bands marching across the island, and travelling and performing music known as C (or just videé) in a manner akin to Brazilian samba schools. Carnival in both islands declined following World War II, bouncing back with new band formats and new traditions only in the 1980s. Both islands feature participatory, call-and-response style songs during their Carnival celebrations.
Ethnic Racial Composition:
* 77% Mulatto
* 10% Black
* 10% White
* 2% Indian
* 1% Others
People:
The population of Guadeloupe is mainly of African or mixed descent of Europeans, Indians (Tamil, Telugu, and other South Indians), Lebanese, Syrians, Chinese, and Carib Amerindians (remnants of the original pre-European population). The archipelago of Îles des Saintes is mostly populated by the descendants of colonists from Brittany and Normandy. It is largely Roman Catholic, speaking French and their dialect (Antillean French).

In 2012 the average population density in Guadeloupe was 247.7 inhabitants for every square kilometre, which is very high in comparison to the whole France's 116.5 inhabitants for every square kilometre. One third of the land is devoted to agriculture and all mountains are uninhabitable. This lack of space and shelter makes the population density even higher.
Languages:
French is the official language of Guadeloupe. They also speak a local dialect of French in informal situations and it is simply referred to as Guadeloupean French or Patois. Guadeloupean French stems mostly from Normandi French spoken in Northern France, with some influences from West African languages. There is also many words of Carib origin.
Religion:
The majority are Roman Catholic, with a minority of predominantly Evangelical Protestant groups.
Economy:
The economy of Guadeloupe depends on agriculture, tourism, light industry, and services. It also depends on mainland France for large subsidies and imports.
Tourism is a key industry; an increasingly large number of cruise ships visit the islands. The traditional sugarcane crop is slowly being replaced by other crops, such as bananas (which now supply about 50% of export earnings), eggplant, and flowers. Other vegetables and root crops are cultivated for local consumption, although Guadeloupe is still dependent on imported food, mainly from France. Light industry features sugar and rum production. Most manufactured goods and fuel are imported. Unemployment is especially high among the young. Hurricanes periodically devastate the economy.
Sports:
Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe.
Videos: